Our endocannabinoid system explained
Like in the case of the opioid system reacting to opioids (morphine, codeine), humans have a distinct receptor system for cannabinoids, compounds found in the cannabis plant. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) contains cannabinoid receptors and influences the activity of many other body systems. The phytocannabinoids of the cannabis plant work in a similar way to our naturally produced endocannabinoids.
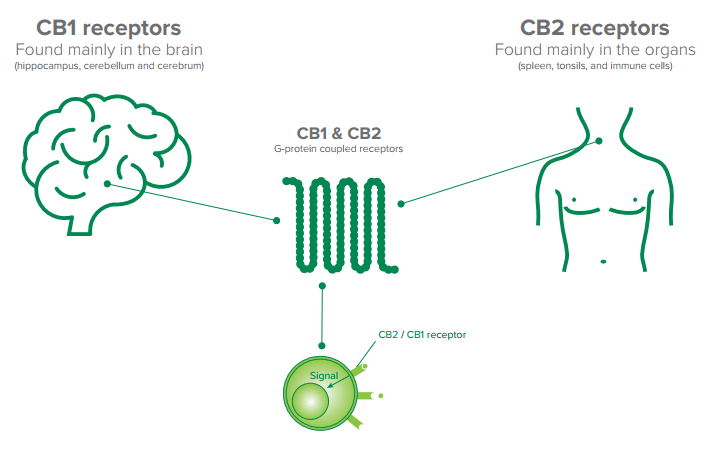
Cannabinoid receptors
The human brain and other organs contain naturally occurring cannabinoid (CB) receptors and the chemicals that bind to them. This is called the human endocannabinoid system. The system’s role is to maintain our body’s ability to function normally by influencing the functioning of other systems. It plays a critical role in our nervous system, and regulates multiple physiological processes. This includes the adjustment of our response to pain, appetite, digestion, sleep, mood, inflammation, and memory.
The endocannabinoid system also influences seizure thresholds (i.e. in epilepsy), coordination, and other processes such as the immune system, heart function, sensory integration (touch, balance, sense of space), fertility, bone physiology, the central stress response system (the HPAA), neural development, and eye pressure.
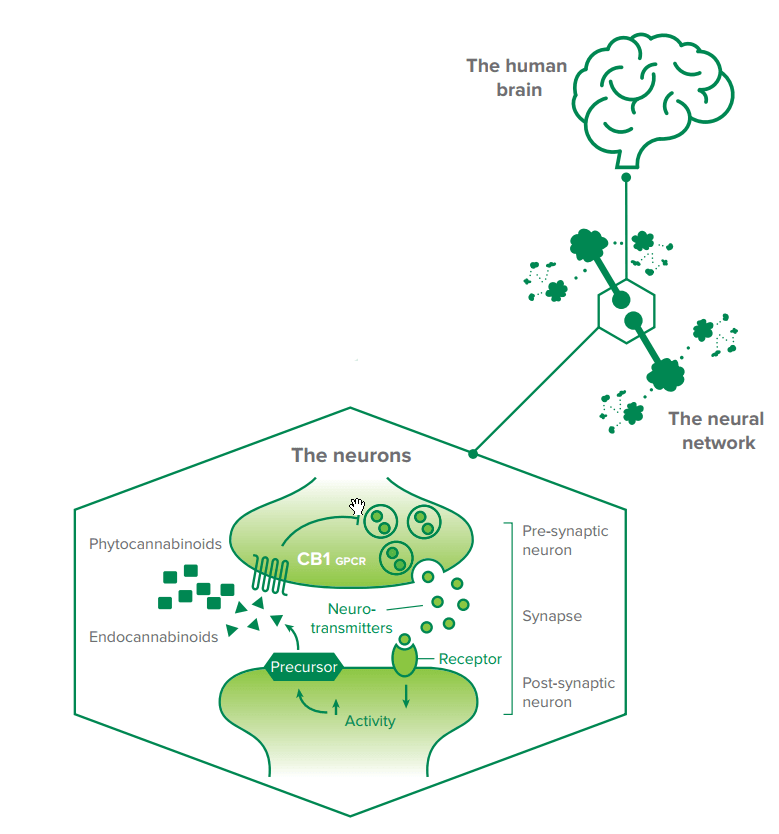
Endocannabinoids
Humans produce their own cannabinoids, the endocannabinoids. These endocannabinoids act on, or stimulate, the cannabinoid receptors. These compounds act in a similar way to phytocannabinoids which also bind to the receptors. The plant cannabinoids are called phytocannabinoids. They are the unique constituents of the cannabis plant. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the main constituents. There are other cannabinoids, but currently far less is known about them.
For example, the CB1 receptor is located in a number of regions of the brain which control various physical and behavioural functions. As a result, cannabinoids influence sensory and motor responsiveness (movement), heart rate, emotional reactions, appetite and nausea/vomiting, sensitivity to pain, learning and memory, and high-level decision making. As our knowledge of the human endocannabinoid system develops so will our understanding of how the phytocannabinoids, THC, CBD and other cannabinoids work. This understanding will lead to better medicines.
GPCRs
Cannabinoid receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs are found on the surface of our cells. These receptors are said to ‘act like an inbox for messages, talking with cells and therefore our body’. GPCRs have a great number of functions in the human body. As a result, many medicines, including medicinal cannabis, work on GPCRs. Humans produce endocannabinoids which interact with the GPCRs CB1 and CB2. We know the most about the endocannabinoids anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Scientific reading about endocannabinoid system & cannabinoid receptors
- Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System
- Cannabinoid receptors: where they are and what they do
- Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease
- Structural basis of signaling of cannabinoids receptors: paving a way for rational drug design in controling mutiple neurological and immune diseases
Also check our own cannabis research page or learn more about medicinal cannabis.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay informed with our latest updates by subscribing to our newsletter for exclusive news and compelling content. Rest assured, we prioritize the integrity of your inbox, delivering quality over quantity, with newsletters dispatched judiciously.