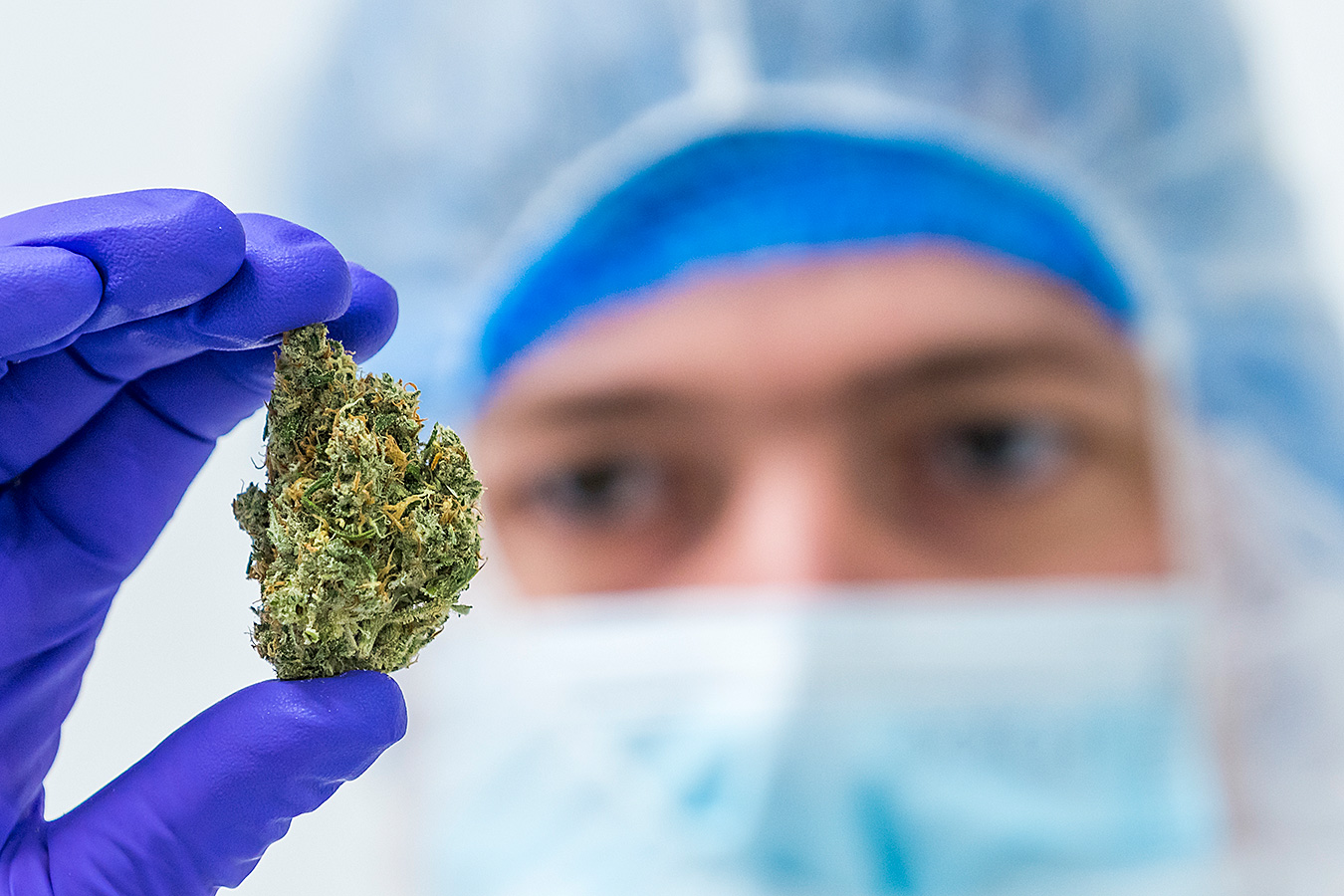
Administration
How medicinal cannabis is taken determines the onset, intensity and duration of any effects. Therefore, choosing the correct administration route, or dose form, is important. The correct route helps patients manage their total daily dosage, the timing and frequency of use. It also helps reduce the risk of side effects. A doctor advises which administration route best suits the treatment outcome and patient needs.
Below, you can find general information about the most common administration routes and dose forms for medicinal cannabis. You can also read about methods pharmacies use to prepare medicinal cannabis for patient use.
- Inhalation (by the lung)
- Oromucosal (inside the mouth/cheek)
- Oral (by mouth)
- Pharmacy compounding
- Cannabis oil
Also read:
Inhalation
Administration

Device

Onset

10 – 30 minutes
Duration

1-3 hours
Administration via the lungs is a very common route. This is because of the rapid absorption of the cannabinoids by the lungs (i.e. THC and CBD). A medical device is necessary to ensure safer and consistent administration. Using a medical device, doctors can advise patients how to gradually reach an optimal dosage (dose titration). There are currently three registered medical devices that were developed specifically for the medicinal use of cannabis:



Volcano Medic – a table top vaporizer device that produces a vapour of cannabinoids from dried cannabis flowers. It is also suitable for vaporizing dronabinol dissolved in alcohol.
Mighty Medic – a portable vaporizer device that produces a vapour of cannabinoids from dried cannabis flowers.
SyqeAir – an EU-GMP-certified inhaler developed for professional healthcare use in hospitals or by licensed patients. It delivers metered and consistent doses of cannabinoids from full-spectrum cannabis in the form of aerosols. The device is currently only available in Israel and Australia.
Oromucosal
Administration

Dose Type

Onset

2 – 4 hours
Duration

6 – 8 hours
With the oromucosal administration, the cannabinoids (THC and CBD) are absorbed through the mouth’s mucosa (the mucus membrane lining the inside of the mouth). The dose is usually administered sublingually (under the tongue) or buccally (inside the cheek) in the form of a solution, spray, or rapidly dissolving wafer. Among the products commonly administered via the oromucosal route are cannabis oil extract solutions.
Oral
Administration

Dose Type

Onset

2 – 3 hours
Duration

6 – 12 hours
Oral cannabis-based preparations are similar in form to other medicines patients may already take. Products for oral administration can come in the form of solutions, tablets, or capsules. However, oral dosing can result in very low absorption of TCH and CBD. It is estimated that up to 6% of the total taken, only, is absorbed. That is because cannabinoids undergo extensive first‐pass metabolism in the liver when swallowed. Lower blood concentrations and a delay to reach peak blood concentration (approx. 120 min) slow the onset of action and duration of effects.
Pharmacy compounding
A compounding pharmacy can prepare medicinal cannabis in a specific formulation and dosage form, such as tablet, oil, capsule, spray or ointment. This depends on the doctor’s prescription. These pharmaceutical preparations must meet legal quality requirements. For example, just as for registered medicines, requirements are imposed on the raw materials used for these preparations. However, there is inconsistency in regulations and compounding methods, resulting in variability in cannabinoid content between different preparations and pharmacies.
Cannabis oil
CBD extracts and full-spectrum cannabis extracts (containing cannabinoids, terpenes and other plant components) are commonly referred to as cannabis oil. Cannabinoids are extracted from the flowers or leaves of the cannabis plant, often using a solvent extraction process (CO2 or ethanol). The extracts are put into solution (formulation and dose) to be administered either sublingually or orally. Cannabis oils in solution may be produced by pharmacy compounding as a magistral preparation. They are also produced by industry according to pharmaceutical standards.
Tea, edibles and smoking
Other administration routes such as teas, edibles and smoking are not discussed in further detail here. The effects of cannabis tea or edibles, such as cannabis-infused brownies and gummies, are unpredictable and not supported by clinical research. Smoking is also not considered a suitable administration route, as it is very harmful to health.
Disclaimer
The information on this page shares general information about the most common routes of administration for medicinal cannabis, which is an unregistered pharmaceutical preparation. It does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional, nor does it promote the use or the efficacy and safety of medicinal cannabis products. Furthermore, it does not aim to promote or provide guidance on the use of products produced by Bedrocan.