Brain scans show effects of CBD on psychosis
What happens in the brain of psychiatric patients when they are given CBD? And especially patients with psychosis? Lead Researcher Matthijs Bossong, who works for Bedrocan, was so fascinated by this question that he spent three years collecting data at the University Medical Center Utrecht to gain more insight into the effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on the brain.
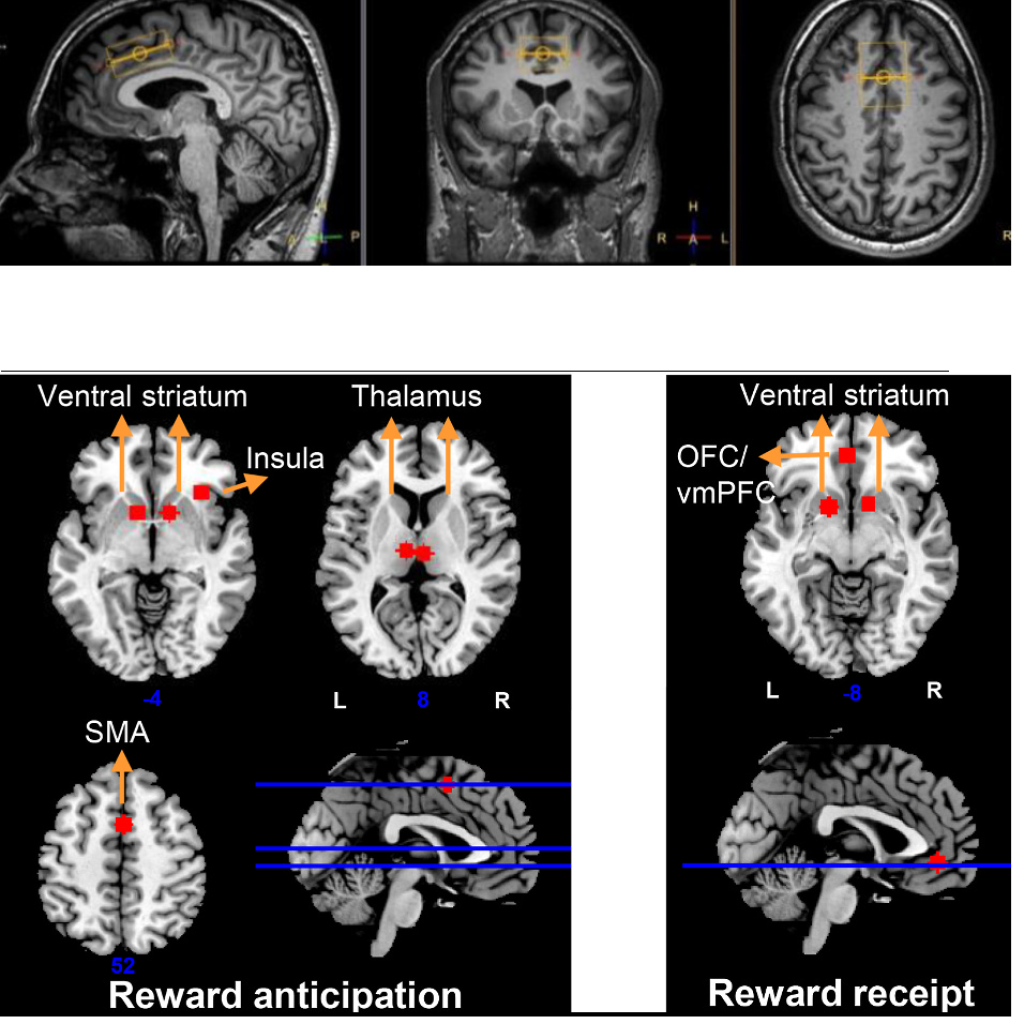
During the study, 31 patients received a capsule containing 600 milligrams of either CBD or placebo every day for four weeks. Before and after treatment, MRI scans were performed and compared. From the scans, it emerged that CBD has a positive effect on the brain connections involved in psychosis. Bossong: “After use, connectivity between brain regions normalised. Previous studies had already shown that CBD may have a positive effect on the complaints and symptoms of patients. We have shown for the first time which mechanisms in the brain are involved.”
Why did you find it important to show what CBD does to the brain?
I have always been fascinated by deviant behaviour, and in this study, I also spoke to patients who could hardly distinguish truth from fiction. A psychotic disorder is a very serious brain disease in which people suffer from delusions and hallucinations. However, the available medication has limited effectiveness in a significant group of patients with psychosis. There is, therefore, an urgent need for new medication. After concluding in my PhD research that the administration of THC, the psychoactive substance in cannabis, to healthy volunteers, results in a ‘psychosis-like’ brain function, I came up with the idea of checking whether the treatment with CBD for patients with psychosis might lead to the normalisation of abnormal brain function.
What happens in the brain of someone with psychoses?
We know that a number of brain functions are altered in patients with a psychotic disorder. For example, the connection, the connectivity between a number of important brain areas is disrupted in patients in the so-called ‘default mode network’. This is a network of brain regions that are active when your attention is directed inward, on your own thoughts and perceptions. Disrupted connectivity in the default mode network is therefore implicated in the experience of delusions and hallucinations.
How can you see on an MRI scan if connectivity in the brain normalises after CBD use?
Functional connectivity means that certain brain regions are active at the same time. For example, when you dream away in your own thoughts, certain brain areas become jointly active, while other areas show activity when performing a difficult memory task. You can measure this coherence in activity by performing a number of calculations on the functional MRI scans that have been performed.
Did the patients participating in the study also feel better?
We have shown in this study that normalisation in brain function after CBD is associated with a decrease in complaints and symptoms. Patients who showed an improvement in brain function after CBD treatment also experienced fewer psychotic symptoms. This indicates that the effects of CBD on brain function are involved in the clinical improvement of patients.
Cannabis use can also trigger psychoses. Does your research also say anything about this fact?
The substance in cannabis responsible for the relationship between cannabis use and the onset of psychosis is THC. CBD is, as it were, the counterpart of THC. While THC can trigger psychosis, our research contributes to the idea that CBD, on the other hand, has antipsychotic properties.
The results of the study have now been published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay informed with our latest updates by subscribing to our newsletter for exclusive news and compelling content. Rest assured, we prioritize the integrity of your inbox, delivering quality over quantity, with newsletters dispatched judiciously.